What Is a Maturity Model in ITIL & ITSM?
Businesses and organizations constantly need to monitor performance and identify areas of improvement. Maturity models are a tool, often used in IT departments, customer-centric organizations, and software companies, to measure the success of management processes, styles, and IT systems.
In this article, we are focusing on the use of the following maturity models in companies' operations:
- Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL)
- Information Technology Service Management (ITSM)
Both are areas where operational, management, and software efficiency is mission-critical for the overall success of an organization. ITIL and ITSM functions impact every part of most businesses. Many couldn't function without one or the other, or both, so it's crucial that maturity model tools are applied to continually assess, iterate, and improve on ITIL and ITSM operations.
What Are Maturity Models Used For?
Maturity model definition
Firstly, let's define, what is a maturity model?
Maturity models are often shrouded in complex jargon, making them difficult to implement. Unlike Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and other process and data-driven process improvement methodologies, maturity models aren't actually difficult to understand. However, when they're implemented effectively, maturity models can make a noticeable difference to ITIL and ITSM operations and teams.
According to Process Street: "A maturity model shows how capable an organization or system is of achieving continuous improvement".
It's a way of assessing current IT performance and outputs (e.g. KPIs, customer success scores, etc.) — using quantitative and qualitative data — looking at what you want to achieve within a fixed timescale. But that's not all. Crucially, "maturity" in any organization, including ITIL and ITSM teams, is assessed on "how good your organization or system is at self-improvement."
It's not simply two milestones; e.g., we are here, and we want to get there. Maturity models are tools for assessing how well an organization or team can get from A to B. In other words:
- Have you, as an operational function, made improvements and iterations in the past?
- What have you learned from them?
- How skilled are you at making ongoing improvements?
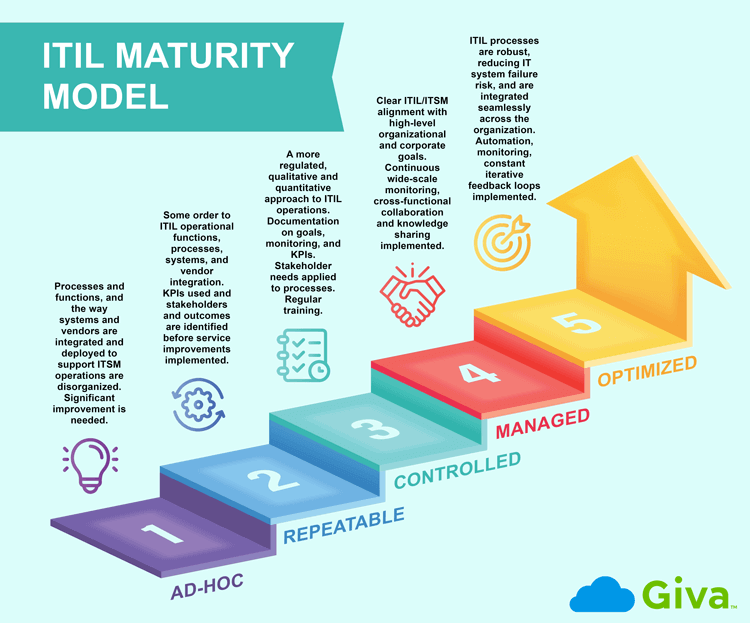
Maturity models measure operational improvement milestones on an upwards curve, from ad-hoc to optimized. Repeatable, controlled, and managed are milestones on the way towards optimized organizational self-improvement, and this applies to ITIL and ITSM departments as much as any within a business.
How Is an IT Maturity Model Used in ITIL?
An ITIL maturity model framework can take an ITIL function through the following steps:
-
Ad-hoc: ITIL functions play a key role in how organizations implement ITSM functions, aligning IT systems and processes with business goals. At this stage of the maturity model, processes and functions, and the way systems and vendors are integrated and deployed to support ITSM operations are disorganized.
Significant improvement is needed when a maturity model assessment identifies that an ITIL and ITSM functions are only at the ad-hoc, or initial stage of operational maturity.
-
Repeatable: At this stage, an organization has attempted to bring some order to ITIL operational functions, processes, systems, and vendor integration. Although far from perfect, KPIs are now in use and stakeholders and outcomes are identified before any service improvements are implemented.
-
Controlled: At the controlled, or defined level, there's a more regulated, qualitative and quantitative approach to ITIL operations. For example, organizations at this stage of maturity have usually:
- Documented ITIL functions and how they relate to ITSM and business objectives and goals, with clear and continuously monitored KPIs and other performance indicators
- Implemented appropriate measures and processes
- Applied corporate knowledge, approaches, and an awareness of external stakeholder needs, including customers, to ITIL process execution
- Provided regular training to ITIL and ITSM staff, with far greater integration and coordination between IT functions and vendors
-
Managed: At this level, the fourth within the ITIL maturity model framework, organizations should have implemented the following:
- A clear alignment between high-level organizational and corporate goals and objectives and ITIL and ITSM functions
- Continuous wide-scale monitoring of appropriate metrics, including KPIs, OKRs, Service Level Agreements (SLAs), response times, and internal and external customer help desk satisfaction scores
- IT Software as a Service (SaaS) automation monitoring tools are widely used
- Cross-functional collaboration and knowledge sharing has been facilitated and is contributing to performance improvements and iterative best practice learnings
-
Optimized: At the fifth and final maturity model level, ITIL processes are robust, reducing the risk of IT systems failures, and they are subject to strong governance controls.
Automation and monitoring tools are implemented throughout every system and process touchpoint. At this stage, there are constant iterative feedback loops, and carefully managed, consistent governance controls across ITIL and ITSM functions. Naturally, at this stage in the maturity model, ITIL operations are integrated seamlessly across the organization.
How Is an IT Maturity Model Used in ITSM?
An IT maturity assessment is something that organizations should factor in before making further ITSM improvements.
Gartner suggests that "90% of organizations will invest in an ITSM tool without first factoring in their maturity."
In most cases, the gap between ITSM service levels an organization needs and what's currently being achieved comes down to the maturity level of an ITSM function. Ad-hoc and undocumented IT processes are always going to produce poor outcomes, including missed SLAs and KPIs.
ITSM teams can apply the same maturity model framework outlined above to achieve continuous improvements. Once this model is applied, you can use it to benchmark where an ITSM function is every quarter, to assess the outcome of iterative changes being implemented.
Now let's take a look at a few ITIL & ITSM assessment tools that organizations can use to assess maturity levels and make improvements.
IT Maturity Assessment Tools for ITIL & ITSM
-
Info-Tech Service Management Maturity Assessment Tool
Info-Tech Research Group is an IT sector research and training organization, with over 30,000 IT professional members worldwide. Info-Tech offers members and non-members alike, a Service Management Maturity Assessment Tool, which you can unlock and use for free.
Using this tool, you can assess your ITIL and ITSM level of maturity, "as well as percentage of completeness for individual processes." The tool helps and guides IT leaders through a phased process which culminates in an IT service management roadmap.
-
Gartner IT Score
Before investing in any ITIL or ITSM assessment tool, it's worth reading Gartner's 6-point checklist, outlining what to look for and how to assess IT maturity levels.
Gartner says to "Start by determining your organization's current level of Infrastructure and Operations (I&O) maturity, as well as the desired state of the organization in 3 – 5 years." I&O includes ITIL and ITSM functions. Gartner recommends that you should invest in ITIL and ITSM assessment tools depending on your organization's level of IT maturity.
One way to check this is with the Gartner IT Score benchmarking framework tool.
-
Axelos, ITIL® 4: the Framework for the Management of IT-Enabled Services
Axelos, now a PeopleCert company, started out as a joint venture between the UK Government and outsourcing giant Capita, in 2014. Not only are they the organization behind the PRINCE2 best practice standard, they also created the ITIL best practice standards and methodologies.
ITIL maturity models, processes, frameworks and certifications are now onto their fourth iteration, for those wanting to align with Axelos, where these originated. Axelos is the governing body responsible for ITIL best practice frameworks, including maturity models for ITIL teams.
According to Axelos, "The ITIL 4 certification scheme can be adapted to the learning requirements of the individual and the organization. It uses a modular, tiered approach to allow you to develop a comprehensive view of service management or to focus on specific areas of knowledge."
Approach this as a framework and set of modular training tools, rather than an ITIL or ITSM software solution.
Although there are many software solutions out there to support IT service and maturity improvements, the best way forward is to assess your level of maturity first, and then find a suitable tool to take the organization and IT functions forward.