Understanding Vulnerabilities in Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare
What is Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)?
If you've ever received a medical bill or had to deal with insurance claims, you may have wondered how healthcare providers manage their finances. That's where healthcare Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) comes in. Essentially, RCM is the process of managing the financial transactions between healthcare providers and patients throughout the entire healthcare experience.
At its core, RCM involves verifying patient insurance coverage, submitting claims to insurance companies, and processing patient payments. The ultimate goal is to ensure that healthcare providers receive proper compensation for their services while making it easier for patients to navigate the billing and payment process.
While the basic principles of RCM apply to all healthcare providers, its implementation can vary depending on the size and structure of the healthcare organization. For instance, a solo practice doctor may have a simplified RCM process compared to a larger healthcare organization with multiple departments and revenue streams.
Regardless of the size of the healthcare provider, RCM is an essential part of the healthcare industry. It ensures patients receive care while helping healthcare providers maintain financial stability.
6 Key Steps in the Healthcare Revenue Cycle Management Process
Revenue cycle management in healthcare is a critical process designed to ensure patients, providers, and payers are on the same page about the medical billing and reimbursement cycle. For healthcare organizations, ensuring timely collection means they can continue to provide a high level of care using the most up-to-date technology. For patients, the process provides clarity around their obligations when receiving care and those of their insurance provider (the payer, if applicable).
The following six steps provide an overview of the main components of the Revenue Cycle Management process.
- Patient registration: The first step involves collecting and verifying patient information such as insurance details, demographics, and medical history. This step ensures that the patient's information is accurate and complete before they receive care. After this step, a patient can begin scheduling and attending regular appointments.
- Charge capture: This step involves capturing all the services and supplies provided to the patient during their visit. It ensures that all charges are recorded accurately to avoid any revenue loss.
- Claims submission: The medical billing team initiates the billing process by inputting the claim charges into a medical billing system or onto a CMS-1500/UB-04 form. Afterwards, they generate the claim and transmit it electronically or through paper to the clearinghouse, which processes it on behalf of the patient's insurance provider, who could be a government or commercial payer. Depending on coverage parameters, some insurance plans will require the patient to pay a deductible fee per reimbursement.
- Denial management (if necessary): After a claim, there may be instances of follow-ups on late payments or denials of services not covered. In the case of a denial, the healthcare provider can investigate the reasoning and resubmit the claim with amendments (if valid).
- Payment posting: This step involves recording the payment received from the payer or the patient, matching it to the corresponding claim, and posting the funds to the patient's account.
- Patient collections/follow-up: This step involves collecting the patient's outstanding balance after the insurance has paid their portion. This can be a straightforward process, though it can also involve patients unwilling to pay for reasons often attributed to misinterpretation of benefits, declined claims, expensive healthcare services, or other monetary challenges. As a result, it becomes the responsibility of the healthcare provider to reach out to the patient and retrieve the remaining balance.
Alternate Example:
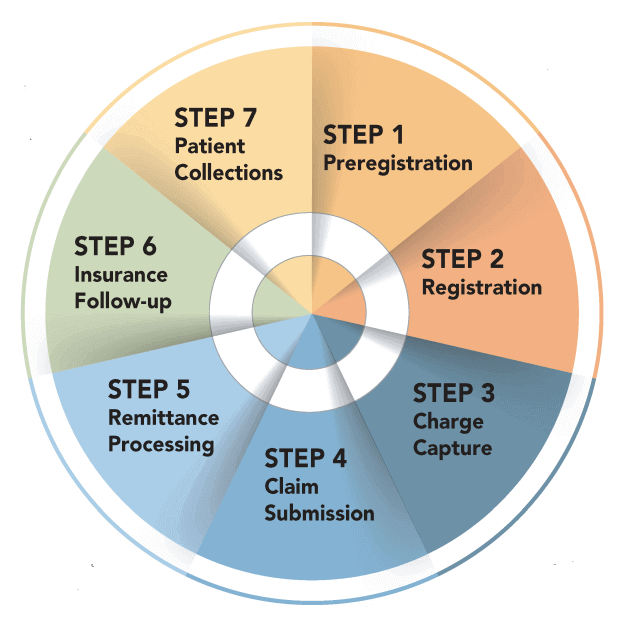
The revenue cycle management process can vary in its number of steps depending on the organization and its stakeholders. Each healthcare organization will have its own unique process based on the software it uses, the payers it works with, and its patients' needs. For example, the RCM process depicted in the image above includes an additional step of preregistration and may have other categories that differ from the process outlined in our example. It's worth noting that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to RCM and that the process is subjective.
Vulnerability Assessments in Healthcare RCM
Vulnerabilities in revenue cycle management can wreak havoc on an unprepared organization. A vulnerability assessment in the RCM process is an evaluation of the organization's procedures, systems, and controls to identify weaknesses and potential threats that could impact its ability to generate or collect revenue.
This assessment is a critical step, as it helps identify areas where the organization may be vulnerable to errors, fraud, or other risks that can result in revenue losses. By conducting a vulnerability assessment, organizations can proactively identify potential issues and take corrective action to minimize or eliminate these risks, thereby improving the efficiency and effectiveness of their RCM processes. Compared to other steps in revenue cycle management, such as charge capture or claims processing, vulnerability assessment is a more proactive approach that can help organizations prevent revenue losses before they occur.
A few items to include in your RCM vulnerability assessment would be:
- Check for any manual processes or workarounds that can introduce errors or risks. Sometimes automating tedious tasks can reduce the chance for error.
- Identify areas where staff training or education may be needed to improve revenue cycle management. For example, you may consider assigning a specific person or group of employees to oversee the process.
- Analyze data to identify patterns and trends that may indicate vulnerabilities or risks.
The Bottom Line: Prioritize HIPAA-Compliance in the Revenue Cycle Management Process
While recognizing the importance of revenue cycle management, safeguarding PHI is equally important. The healthcare industry must prioritize protecting patient information throughout the RCM process. As we've discussed, there are many ways in which RCM can be vulnerable to cyber threats, such as phishing attacks, malware, and data breaches. However, there are ways to mitigate these risks, such as through regular vulnerability assessments.
HIPAA sets national standards for protecting sensitive health information, and compliance with its regulations is essential for safeguarding patients' data. By partnering with a HIPAA-compliant technology provider, healthcare organizations can ensure their RCM processes are secure and their patients' data is protected. This process should account for the storage of PHI and the exchange of information between the provider, payer, and patient.
Learn more: Giva's dedication to HIPAA compliant offerings
It's important to note that RCM companies are also held to the same high standards as healthcare organizations regarding HIPAA compliance. This means they must comply with the same regulations and standards to ensure the security and privacy of patients' information.
By taking these precautions, healthcare organizations can ensure their patients' information is secure and protected throughout the RCM process. This is essential for maintaining patients' trust and ensuring the continuity of healthcare operations.