The Difference Between Help Desk, Technical Support & Desktop Support & Skills Required
With continued growth in computer and hand-held device use in the lives of many brings increasing technical questions and problems that arise. And so, the field of supporting these systems grows along with it, which brings business opportunities for entrepreneurs, and employment opportunities for support personnel.
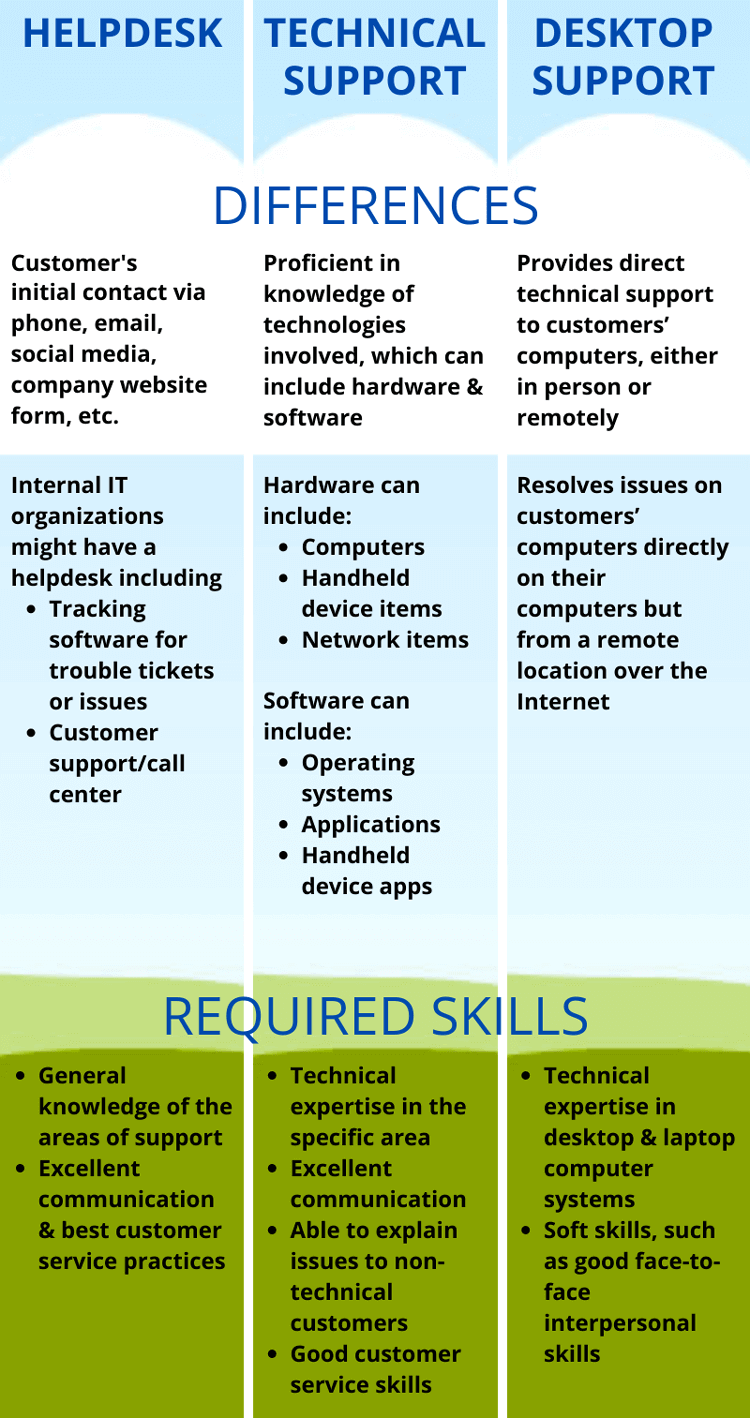
But there are different types of support needs accompanied by varying required responsibilities and skills. The following are the differences between, and skills required for, three common areas of support: Help Desk, Technical Support, and Desktop/Deskside Support.

IT Help Desk
This is usually your front-line (sometimes called Level/Tier 1) level of support – the place where your customers will make initial contact; and this contact can be via many different channels: phone, email, social media, company website form, etc.
Internal IT departments might have a helpdesk; and computer, handheld device and software vendors will typically have a customer service/call center. Often these can be outsourced as well.
Usually, a helpdesk will have some form of tracking software for trouble tickets or issues.
Help Desk Support Skills List:
- General knowledge of the areas of support, including hardware or software and apps. It is customer service best practices to be able to answer questions at this level, if at all possible
- How to communicate regarding those areas, and understanding the customers' needs well, especially when customers are not able to clearly describe their issues
- High degree of soft skills, such as good communication and best customer service practices (especially patience and empathy) with excellent interpersonal communication
IT Technical Support
These people will know most about the technologies involved that relate to the customers' issues (they are sometimes referred to as Level/Tier 2 or 3 support).
This can include hardware and software:
- Hardware can include:
- Computer and handheld device items, such as displays, hard drives, memory, motherboards, etc.
- Network items, like routers, switches, networks servers, etc.
- Software can include:
- Operating systems, such as Windows, Linux, Apple OS, etc.
- Applications, such as Microsoft Word, a web browser, conferencing software such as Microsoft Teams or Zoom, etc.
- Handheld device apps.
IT organizations and hardware/software vendors will need experts in all of the above as related to their business technologies.
Technical Support Skills List:
- Technical expertise in the specific area, often including both hardware and software or apps
- Soft skills, such as good communication and being able to explain issues to non-technical customers, and good customer service interpersonal skills
IT Desktop/Deskside Support
These people provide direct technical support to customers' computers, either in person or remotely.
Internal IT departments as well as computer hardware vendors will often have people that can come out and fix computer problems in person.
Remote computer management has helped in allowing this type of person to resolve issues on customers' computers directly on their computers but from a remote location over the Internet.
Desktop Support Skills List:
- Technical expertise in desktop and laptop computer systems
- Soft skills, such as good face-to-face interpersonal skills
Important Conclusion
While the level of technical expertise can vary from role to role, interpersonal people skills is one important area that not only cannot be neglected, but should be highly emphasized in a support organization and a skill highly sought after in support personnel. All customer-facing people represent the company and can help or hurt the business' bottom line; and so, while technical skills are a must, great customer service skills and interpersonal relationship abilities are imperative as well.